API security for desktop owners
OpenFin API security enables desktop owners and application providers to determine the API calls that are available for an OpenFin application. Applications must declare in their manifest that they use security-sensitive APIs (secured APIs) for functionality that is outside the security sandbox, such as launching an external application or using fullscreen mode. While these features can be beneficial, OpenFin understands that desktop owners may need to restrict certain APIs from running on a desktop computer, particularly from an unknown or untrusted application. API security gives the Desktop Owner tools to prevent application developers from implementing features that may be deemed sensitive to an organization.
In order to leverage secured APIs, application providers must declare the use of specific API functions in their application manifest file, and explicitly declare API functions used via domain settings. This assists desktop owners to recognize API intent up-front. If an API function is not permitted by the organization or needs to be enabled for ease of application functionality, as the desktop owner, you can define settings to block or allow use of the API function.
For versions of OpenFin prior to v20, if a desktop owner does not block an application’s use of a secured API, it is permitted. Starting in v20, if the desktop owner (or their delegate) does not explicitly allow a secured API for an application, it is blocked by default.
Versions of OpenFin between v20 and v24 automatically allow secured APIs if the runtime fails to connect to the RVM or if the RVM doesn't exist. Starting in v24, secured APIs are blocked if the RVM cannot be reached (due to messaging failures) or if the RVM doesn't exist (the runtime was launched from the CLI).
Note
As an alternative to controlling secured APIs through desktop owner settings, an application can use a trusted application configuration, which grants permission to use requested APIs after validation by the RVM.
However, desktop owner settings for secured APIs, if defined, take precedence over a trusted application configuration.
This article describes settings that can be made by desktop owners to control secured APIs.
For complete details about secured APIs, see API security.
Prevent local development
To simplify the environment for application development, if the application is running from localhost, only the app manifest declaration is needed to access the API; no desktop owner setting or other permission is required.
As a desktop owner, to prevent this exception for developers’ desktops, define the following registry key as a DWORD value set to 0 : HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\OpenFin\RVM\Settings\enableSBDLocalhostTrusted
If this key is not defined or is set to a non-zero value, the exception for localhost is allowed.
Delegate control
A desktop owner has the ultimate control over whether to allow or block a particular API for a particular application; you can delegate the decision to the end-user.
End-users are prompted to allow an application to use a requested API in the following cases:
-
You explicitly delegate control to them.
-
You do not define access for that combination of application and API.
The dialog box presented to the user lists the actions represented by the APIs (not the API names themselves), with a link to Review security permissions for detailed information.
-
If the user blocks the use of the APIs, then the application still runs, but it doesn’t have access to the requested APIs and the user will be prompted again on the next launch.
-
If the user allows the use of the APIs, they aren’t prompted again on future launches.
-
If the application is updated and requires new secured APIs that aren't blocked or allowed by the desktop owner or OpenFin, then the user is prompted again, for the new permissions.
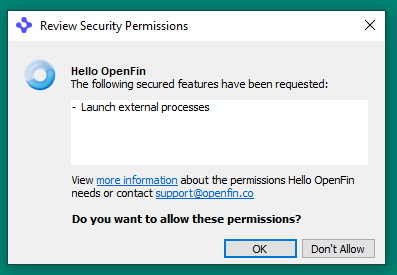
This dialog box can be customized through the following settings: (starting in RVM 6.9)
-
App icon: The
icondefined for the application's shortcut in shortcut settings in the app manifest; used next to the application name in this dialog box. -
Email address: The same
emailas is defined in the support information. -
"more information" link target: A URL defined by the
securityPermissionsMoreInfoUrlproperty of the startup_app or platform object in the app manifest.
Configure Desktop Owner settings
The primary mechanism for desktop owners to control access to secured APIs is through definitions in a desktop owner settings file. For information about other settings, refer to Desktop owner settings.
Starting in RVM version 7.0, the RVM reads the DesktopOwnerSettings registry key and the desktop owner settings file each time an application is launched; it uses the values as defined at that time for that instance of the application. This feature enables desktop owners to update settings values, including those related to application security, without terminating the RVM or other running applications, possibly by pointing to a completely different file. For already-running applications, the settings values remain as they were defined at the time that the application was launched. All settings related to application security can be refreshed in this manner.
Application security settings
To define API security settings for specific applications, there must be an object named applicationSettings at the top level of the JSON file. The members of this object are key strings. A key can be any of the following:
-
A manifest URL
-
An arbitrary label; in this case, its
urlsmember is a list of strings representing a collection of Chrome match patterns for manifest URLs. This enables you to define one set of API security settings for a group of applications that have similar manifest URLs. -
The string
default, which applies to any application whose manifest URL does not match another key.
Within each sub-object of applicationSettings, a permissions object contains the settings for specific APIs, grouped by namespace. Values may be Booleans or objects with further members. (Refer to the Permissions interface.) If an application declares that it uses an API, and no matching permission definition sets a value for it, then the end-user is prompted to allow or disallow it.
The System.readRegistryValue() method supports more granular control. The enabled member key controls use of the method. In addition, the registryKeys member is an array of registry keys that the application can read when the method is allowed.
For web APIs, as with the app manifest, the name of the API is sufficient to indicate that it is allowed.
Global default permission
You can set a global default for handling cases where the combination of the application and the requested secured API is not covered by the application-specific settings under applicationSettings.
This option is defined in the desktopSettings object.
securedAPIDefaultPermission: Possible values are”allow”,”deny”, or”prompt”(default).
Example desktop owner settings
The following example shows desktop owner settings for configuring secured APIs.
{
"desktopSettings": {
"securedAPIDefaultPermission": "prompt",
...
},
"applicationSettings": {
"https://www.examplefinapp.com/manifest1.json": {
"permissions": {
"System": {
"launchExternalProcess": {
"enabled": true,
"assets": {
"enabled": true
},
"downloads": {
"enabled": true
},
"executables": {
"enabled": true
}
}
}
}
},
"http://www.examplefinapp.com/AnotherApp.json": {
"permissions": {
"System": {
"launchExternalProcess": {
"enabled": true,
"assets": {
"enabled": true
},
"downloads": {
"enabled": true
},
"executables": {
"enabled": true
}
},
"readRegistryValue": {
"enabled": true,
"registryKeys": [
"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\OpenFin\\RVM",
"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\OpenFin\\Runtime",
"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Oracle"
]
}
},
"webAPIs": [
"audio",
"video"
]
}
},
"MyAlias": {
"urls": [
"https://example.com/*.json",
"https://*.example.com/*.json"
],
"permissions": {
"System": {
"launchExternalProcess": {
"enabled": true,
"assets": {
"enabled": true
},
"downloads": {
"enabled": true
},
"executables": {
"enabled": true
}
},
"readRegistryValue": {
"enabled": true,
"registryKeys": [
"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\OpenFin\\RVM",
"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\OpenFin\\Runtime\\Path",
"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Oracle"
]
}
}
}
},
"default": {
"permissions": {
"System": {
"launchExternalProcess": {
"enabled": false
}
}
}
}
}
}
Updated 6 months ago
