Organize views with layouts
Users with data-heavy workflows often need to be able to combine several sources of information to view at a glance. OpenFin provides the layouts capability to let users do this within a single window, so they can complete their tasks quickly and easily without switching through multiple applications or windows.
Note
This article describes
LayoutConfigwhich saves the current arrangement of views in a window or restores a previous arrangement of views in a window. To understand the Layout APIs that programmatically arrange views andTabStacksin a window, see Arrange views programmatically with layouts.
What are layouts?
Layouts allow you to take multiple standalone web applications and compose them together into a single window. What was once a disparate set of tools and apps that people had to arrange on their desktop can now be shown in a single window, bringing those tools together as a cohesive whole. What’s more, these web apps can be run in separate renderer processes or they can share processes. For more information about render processes, see the Process affinity section in the Container overview article.
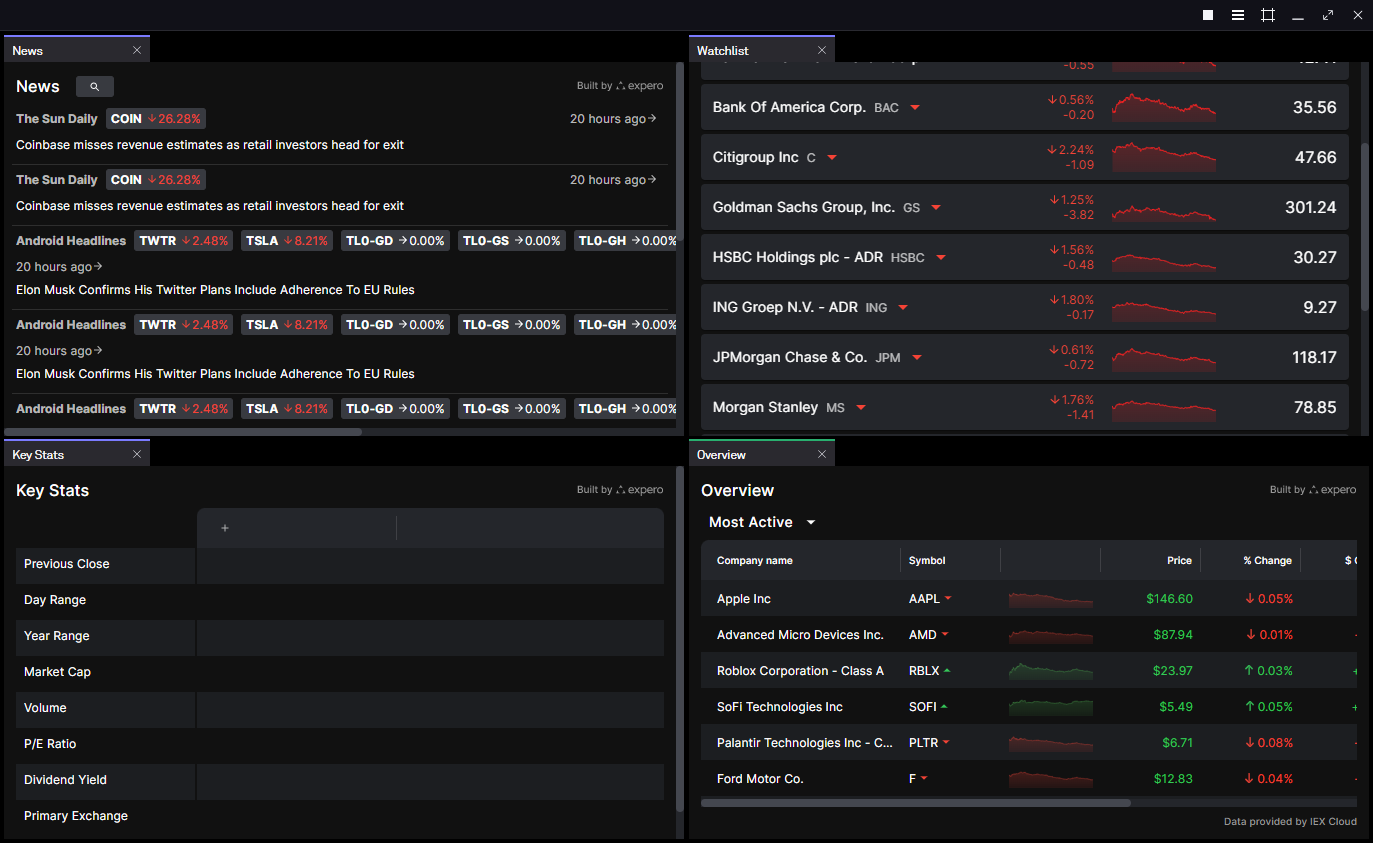
When it comes to representing a layout in code, we can think of layouts as being similar to snapshots.
-
Snapshots are a way to save and restore the positions and configurations of windows on the desktop.
-
Layouts are a way to save and restore the positions and configurations of views in a window.
You can open a window, create views and adjust them to perfection, then save that layout configuration to use in your application.
How to capture a layout
While, technically, you could write the complex JSON of a LayoutConfig by hand, that’s not recommended. Instead, OpenFin recommends that you create your views exactly the way you want them, then capture the LayoutConfig data. You can also capture a layout if a user has modified the arrangement of view from the default; you can then reapply that layout as needed by that user.
The function to use when capturing the LayoutConfig data varies depending on whether you want the layout data from the current window, or from another window.
If you want the LayoutConfig data for the current window, use getCurrent or getCurrentSync.
For getCurrent:
const layout = await fin.Platform.Layout.getCurrent();
// Use wrapped instance to control layout, e.g.:
const layoutConfig = await layout.getConfig();
For getCurrentSync:
const layout = fin.Platform.Layout.getCurrentSync();
// Use wrapped instance to control layout, e.g.:
const layoutConfig = await layout.getConfig();
If you want the LayoutConfig data for a window that is not the current window, use wrap or wrapSync.
For wrap:
const layout = await fin.Platform.Layout.wrap({ uuid: fin.me.uuid, name: '<my_window>' });
// Use wrapped instance to control layout, e.g.:
const layoutConfig = await layout.getConfig();
For wrapSync:
const layout = fin.Platform.Layout.wrapSync({ uuid: fin.me.uuid, name: '<my_window>' });
// Use wrapped instance to control layout, e.g.:
const layoutConfig = await layout.getConfig();
How to apply a layout
After you have a LayoutConfig, you can apply it to the layout of views in a window by using the replace function. This replaces the window’s current layout with the new layout. Any views that do not exist in the new layout are destroyed.
let windowIdentity;
if (fin.me.isWindow) {
windowIdentity = fin.me.identity;
} else if (fin.me.isView) {
windowIdentity = (await fin.me.getCurrentWindow()).identity;
} else {
throw new Error('Not running in a platform View or Window');
}
const layout = fin.Platform.Layout.wrapSync(windowIdentity);
const newLayout = {
content: [
{
type: 'stack',
content: [
{
type: 'component',
componentName: 'view',
componentState: {
name: 'new_component_A1',
processAffinity: 'ps_1',
url: 'https://www.example.com'
}
},
{
type: 'component',
componentName: 'view',
componentState: {
name: 'new_component_A2',
url: 'https://cdn.openfin.co/embed-web/chart.html'
}
}
]
}
]
};
layout.replace(newLayout);
An alternative to creating a LayoutConfig and applying it to the window is to use the applyPreset function. The applyPreset function creates a new layout based on preset arrangements, which include columns, grids, rows, and tabs. If one of those preset arrangements works for your use case, it can simplify the task of presenting a layout.
let windowIdentity;
if (fin.me.isWindow) {
windowIdentity = fin.me.identity;
} else if (fin.me.isView) {
windowIdentity = (await fin.me.getCurrentWindow()).identity;
} else {
throw new Error('Not running in a platform View or Window');
}
const layout = fin.Platform.Layout.wrapSync(windowIdentity);
await layout.applyPreset({ presetType: 'grid' });
Optimizing layouts
OpenFin provides a couple of tools to help you design the right layout for your application.
Layout settings
By using properties in LayoutOptions, layouts can enable or restrict various behaviors for your users. For example:
-
show or hide the maximize button (
showMaximiseIcon) -
enable or disable users from resizing tabs (
preventSplitterResize) -
enable or disable tab headers (
hasHeaders).
Custom platform considerations
When using the OpenFin Platform API, all of the logic and backing for layout operations are already initialized and baked in.
If, however, you have created a custom platform, one additional step is required. You have to call fin.Platform.Layout.init with the initLayoutOptions of the windows that have views controlled by layouts.
For more information on using init in your custom platform, you can read the init API reference and code examples.
Updated 7 months ago
