Customize search results in Home
You can create a custom preview pane for search results that are displayed in Home using custom templates. You can define different responses for a search result depending on which fragment of the pane is clicked.
Similar to notification templates
Custom search result templates are similar to custom notification templates.
Parts of a template
The components of a template are called fragments. You create your template by including the fragments you need in a JSON object.
The set of fragments is similar to that for notification templates:
-
containergroups other fragments, with no visible parts of its own -
textdisplays text -
listdisplays a list of name-value pairs -
imagedisplays an image -
button(unique to search result templates) executes an action
Button fragment
The button fragment enables the user to do more than merely select a search result. The user can interact with the result in whatever way makes sense for your use case. For example, a View Client button would take a different action than a View Instrument button.
In Workspace v16.1 or later, you can also work with a splitButton fragment, which lets you include a button that's explicitly styled for a dropdown. For an example, see the API reference.
Actions
The button, splitButton, image, and text fragments process mouse clicks. Each of these fragments returns an optional action string, which you can use to direct your code. A click on an image could return the string ‘Zoom Image’, which could be used to display a full-size view of that image. A click on the text of a client’s name could return the string ‘Call Contact’, which could be used to start a phone call to that client.
Example action:
const myComposition: TemplateFragment = {
... // Fragment properties
action: 'Call Contact';
}
// CLIProvider.onResultDispatch()
async function onResultDispatch(res: CLIDispatchedSearchResult) {
if (res.action.name === 'Call Contact') {
services.phone.call(res.data.phoneNumber);
}
}
How it works
You create a JSON object to describe how to render your search results. That JSON object contains the fragments you need to display a search result, along with some style information for each fragment.
When the user selects a search result, the result data is rendered and displayed on the user's screen.
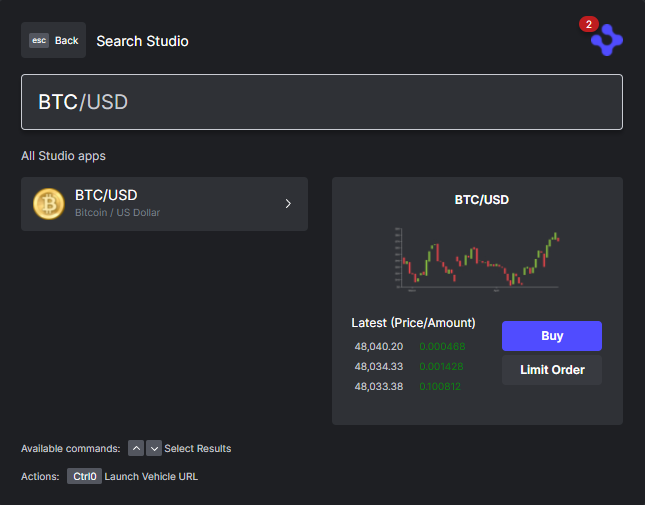
How to do it
Leveraging custom templates for search results requires two phases:
-
Define the custom template JSON object. This JSON object drives a large part of the custom search results.
-
When generating search results, apply the template to the data for each search result.
Templates and fragments
The custom template can be thought of like a simplified HTML render, where the fragments are like simplified HTML elements.
| Fragment | Corresponds to |
|---|---|
| container | <div> |
| text | <span> |
| list | <ul> with no list marker, and with name-value pairs |
| image | <img> |
| button | <button> but with more complex formatting possible |
| splitButton | <button> with more complex formatting plus expandable menu that includes additional <button> elements |
Three fragments have an optional children property; container, button, and splitButton. Just as HTML pages often have a <div> within a <div> within a <div>, custom templates can have a container within a container within a container. The children property enables this.
Because buttons often require flexible formatting, the button and splitButtons fragments can also contain children.
Styles
To continue the analogy with HTML, you can define styling for template fragments, via the style element. The style element can contain React inline style properties such as flex properties, colors, sizes, and fonts. Remember that React style properties use “camelCase” names, such as backgroundColor rather than “kebab-case” names, such as background-color, as in plain CSS.
Do not use position:fixed
The
position:fixedCSS property value is not allowed, to prevent elements from appearing outside their search result card; thecreate()function throws an error if it is used.
Optional fragments
Fragments can be optional. Why is this useful?
Not every fragment that you define is needed for every search result that the template containing it might be applied to. In some cases, the corresponding data might not exist, but the result of the search result is valid.
Data items related to a search result are mapped via the fragment's dataKey property. If a fragment's optional property is true and a value matching its dataKey property is not supplied for a search result, that fragment is not rendered. If optional is false or not defined, then missing data in a search result causes an error for that search result.
Put it together
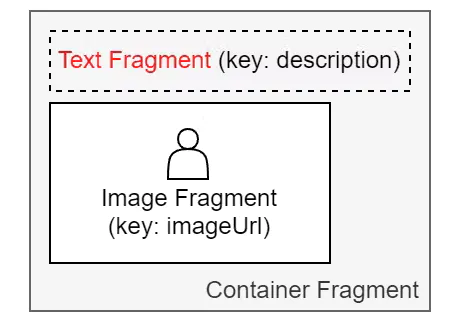
Create the JSON object template. In this case, myComposition:
const myComposition: TemplateFragment = {
type: 'container',
style: {
display: 'flex',
flexFlow: 'column',
// some more styling
},
children: [{
type: 'text',
style: {
color: 'red',
// ...
}
dataKey: 'description', // a key to templateData
},
{
type: 'image',
style: {
width: '200px',
// ...
}
dataKey: 'imageUrl',
}]
}
This code creates a composition that looks like this:
But there is a very important question that hasn’t been answered yet. How do you take the data you found in your search and put it on the rendered display?
You use the dataKey property of the fragment.
To illustrate, let’s say that, as in the template JSON object shown above, myComposition, you have a text fragment of red styled text where dataKey is set to description, and an image fragment where dataKey is set to imageUrl. Let’s further say your search results object also has properties named description and imageUrl.
And in your search result data you have a search result where the description property is set to the text “Company 1” and imageUrl points to an image file of the Company 1’s logo. For example, the first element of mySearchResults as seen here:
const mySearchResults: HomeSearchResult[] = [{
... // standard home search result options
template: CLITemplate.Custom,
templateContent: {
layout: myComposition,
data: {
description: 'Company 1',
imageUrl: 'https://company1.com/logo.png'
}
}
},
{
... // standard home search result options
template: CLITemplate.Custom,
templateContent: {
layout: myComposition,
data: {
description: 'Company 2',
imageUrl: 'https://company2.com/logo.png'
}
}
}];
When the search result is rendered by the custom template, the text 'Company 1' appears as red text in the rendered display, and Company 1’s logo appears below the red text. Likewise, the name and logo for Company 2 are displayed for the search result for Company 2.
Updated about 1 year ago
